Molecular Machines
< General Studies Home Page
Contents
Molecular Machine, or nano-machine, is any discrete number of molecular components that produce quasi-mechanical movements (output) in response to specific stimuli.
The 2016 Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded to ‘Molecular Machine’ trio for the design and synthesis of molecular machines
Details about their contributions
- Sauvage in 1983 took the first step by linking two ring shaped molecule to form a chain

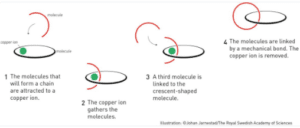
Design and Synthesis of Molecular Machines
- Stoddart in 1991 developed a rotaxane, a dumbbell-shaped molecular structure that enabled him to build molecular lift, a molecular muscle and a molecule-based computer chip.
- Feringa in 1999 was the first person to develop a molecular motor and in 2011 designed a four-wheeled nano-car
Significance of those nano-machines
- These tiny machines that we can’t even see have enormous potential.
- Medicine and treatment
-
- Molecular technology could lead to development of machines that are so small they could be swallowed or implanted into human bodies with little negative effec
- They could be used to fight disease in the body, to repair damaged tissues, and even to probe DNA structure.
- Such precise drug deliver will minimize adverse side-effects.
-
- Smart materials able to adapt to their environment, small sensors that can be controlled remotely, and drugs that are activated on command
- Efficient energy storage devices
- Medicine and treatment
